What Does AGM Battery Mean?
Understanding the technology behind Absorbent Glass Mat batteries
AGM Battery Definition
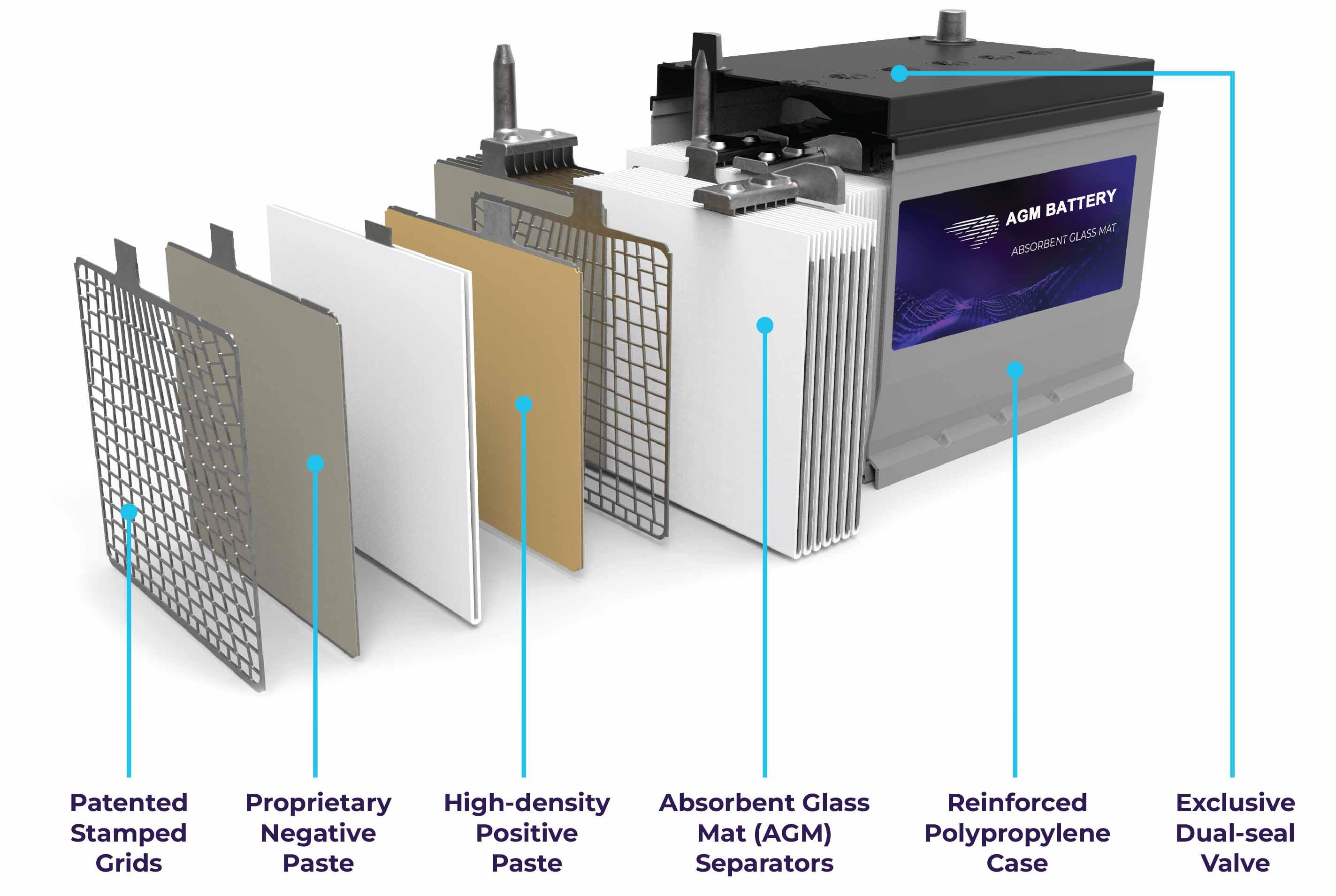
AGM stands for "Absorbent Glass Mat" - a type of sealed lead-acid battery technology where the electrolyte is absorbed into a fiberglass mat separator between the battery plates. This design eliminates the need for liquid electrolyte, making AGM batteries spill-proof and maintenance-free.
The absorbent glass mat acts like a sponge, holding the sulfuric acid electrolyte in place while allowing the chemical reactions necessary for battery operation to occur efficiently.
Key AGM Characteristics:
- Sealed, maintenance-free design
- Spill-proof and leak-resistant
- Can be mounted in any position
- Lower self-discharge rate
Sealed Design
No maintenance required